Ready to streamline your complex Zabbix operations?
I’ve distilled the most valuable insights from this blog into one essential guide. Take full control of your environment with the Zabbix 7 Enterprise Optimization Handbook [Mastering Hybrid Infrastructure Monitoring with a Kubernetes First Approach].
👉 Get your PDF copy here: https://jikimy.gumroad.com/l/zabbixmaster
Related Posts :
(Bare-metal / Kubernetes Pod environments fully supported, Agent2 plugin based)
MySQL monitoring in Zabbix no longer relies on old-style UserParameter scripts.
With Zabbix Agent2 + the MySQL plugin, you can collect all related metrics (InnoDB, Slow Query, Replication, Buffers, etc.).
However, real production environments fall into two completely different types:
- MySQL running on bare-metal (physical/VM) servers
- MySQL running inside a Kubernetes Pod and exposed through a Service External IP
Since the networking models differ completely, the Agent2 configuration also differs.
This guide covers all differences and provides a fully operational configuration method based on Zabbix 7.4.
1. Supported Versions
Zabbix
- Zabbix Server/Proxy 7.4 or later
(The official documentation states that 5.0 or later is also supported.)
MySQL Engines
- MySQL 5.7 / 8.0 / 9.4
- Percona 8.4
- MariaDB 10.6 / 11.8
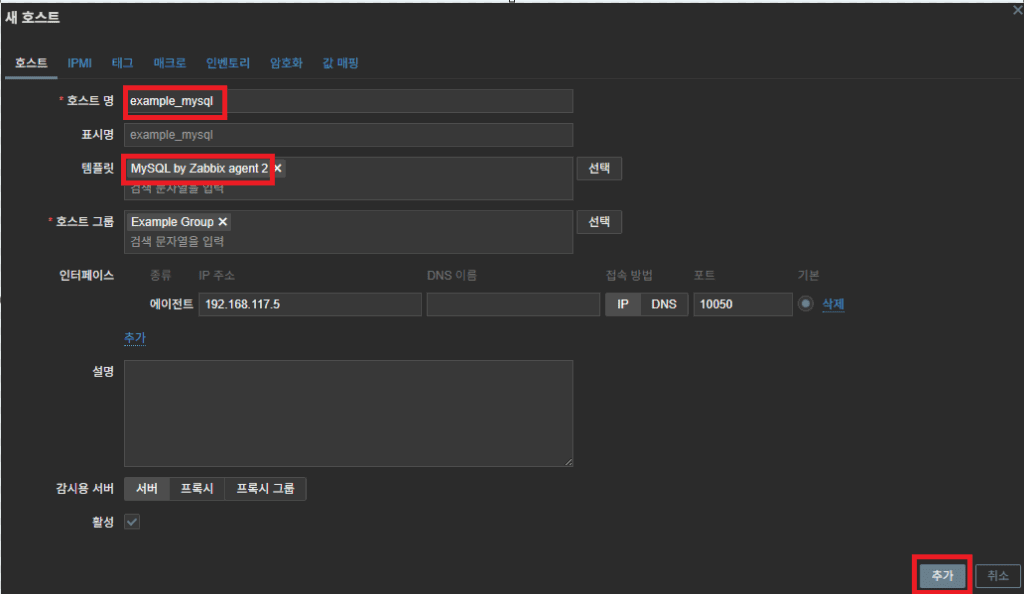
2. Create the MySQL Monitoring Account (Common for All Environments)
Regardless of the environment, prepare the following privileges:
CREATE USER 'zbx_monitor'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>';
GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT, PROCESS, SHOW DATABASES, SHOW VIEW
ON *.* TO 'zbx_monitor'@'%';

Additional privilege required for MariaDB 10.5.9+:
GRANT SLAVE MONITOR ON *.* TO 'zbx_monitor'@'%';
3. Exact Path of the Agent2 Plugin Configuration File
The MySQL plugin must already be installed and enabled in Agent2.
If installed correctly, its configuration file will appear under:

4. Template Macro Method vs Agent2 Session Method
Both methods work, but they behave differently.
✔ Template Macro Method
{$MYSQL.DSN} = tcp://192.168.117.5:3306
{$MYSQL.USER} = zbx_monitor
{$MYSQL.PASSWORD} = <password>
Pros: No need to modify the plugin config file; can configure everything from the UI.
Cons: Password becomes visible in the Zabbix UI.
✔ Agent2 Session Method (Recommended)
After installing Zabbix Agent2 on the target host, modify:
/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.d/plugins.d/mysql.conf
Default:
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.*.Uri=
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.*.User=
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.*.Password=
Modified:
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.Uri=tcp://192.168.117.5:3306
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.User=zbx_monitor
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.Password=<password>

Template macro (in Zabbix Web UI):
{$MYSQL.DSN} = example_mysql

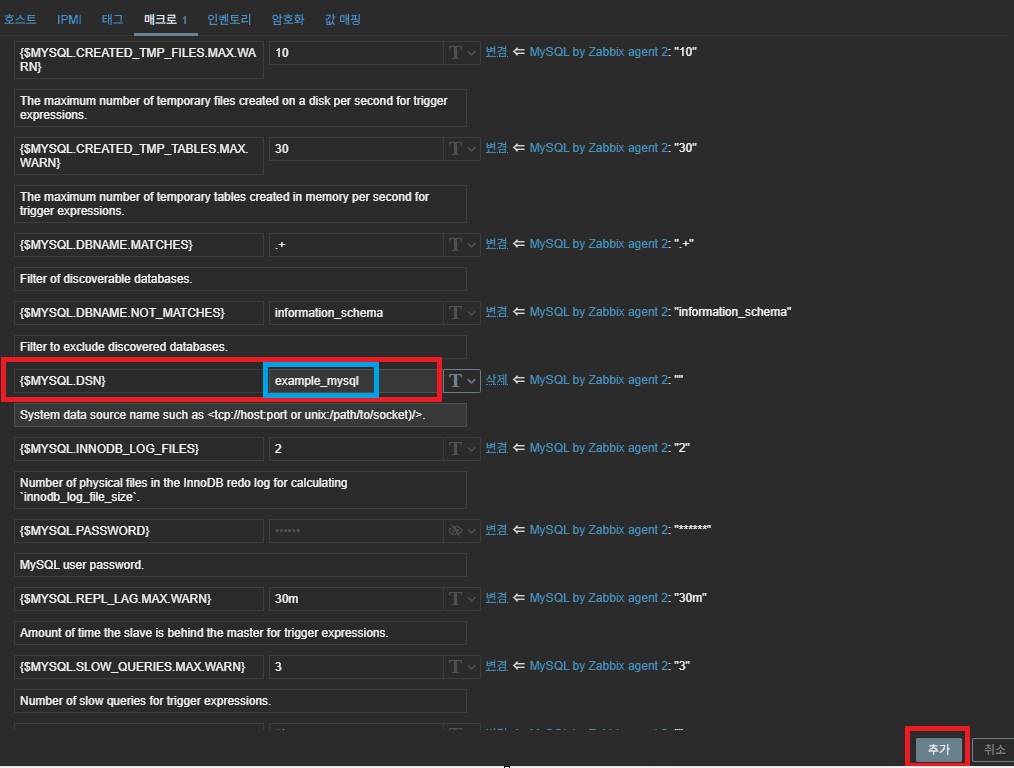
Advantages:
- Password exists only on the Agent2 host
- Supports any number of MySQL instances
- Best security & scalability
- Officially recommended by Zabbix
Tip: Plugin configuration styles
✔ (A) Default-based monitoring for a single MySQL instance
Use when only one MySQL instance exists.
Plugins.Mysql.Default.Uri=tcp://192.168.117.5:3306
Plugins.Mysql.Default.User=zbx_monitor
Plugins.Mysql.Default.Password=<password>
Zabbix template macros can remain empty.
Pros:
- Very simple configuration
- No need for session names
- Ideal for single-instance setups
✔ (B) Session-based structure for multi-instance monitoring
Use when multiple MySQL instances must be monitored.
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.Uri=tcp://192.168.117.5:3306
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.User=zbx_monitor
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.example_mysql.Password=<password>
5. Monitoring MySQL Inside Kubernetes Pods
Agent2 runs on the host,
while MySQL runs inside a Pod.
Because a Pod’s ClusterIP is not accessible from outside, you must expose MySQL through a Service (NodePort or LoadBalancer).
The most practical method is:
Monitoring via LoadBalancer External IP
Flow:
Agent2 (Host) → Service External IP → MySQL Pod
Example External IP:
192.168.117.90:3306
mysql.conf:
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.K8s.Uri=tcp://192.168.117.90:3306
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.K8s.User=zbx_monitor
Plugins.Mysql.Sessions.K8s.Password=<password>
Zabbix macro:
{$MYSQL.DSN} = K8s
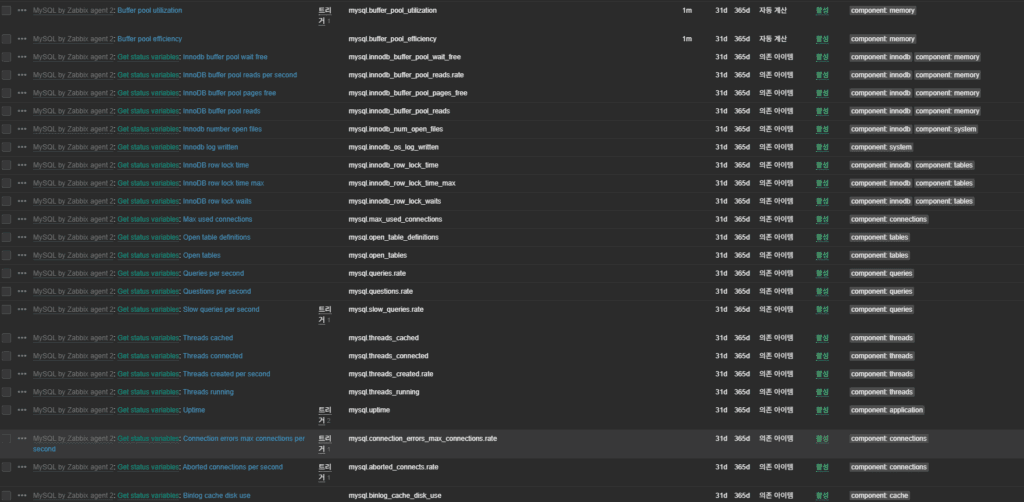
6. Metrics: Main Collected Items
- InnoDB buffer/engine statistics
- Threads / Connections
- Slow Queries
- Temp Table creation ratio
- Buffer Pool Hit Ratio
- Query throughput
7. Troubleshooting Checklist
1) Bare-metal environments
- MySQL config (my.cnf):
Ifbind-address=127.0.0.1, external access fails → change to0.0.0.0. - Unix socket permissions:
Ensure thezabbixuser can read/write/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock. - Firewall:
Make sure OS firewalls or cloud security groups allow port 3306. - SELinux:
If SELinux is in Enforcing mode, Zabbix Agent may be blocked from accessing sockets/ports.
→ Disabling SELinux is recommended.
2) Kubernetes environments
- Kube-proxy mode:
Rarely, IPVS mode may cause intermittent session timeout issues. - NetworkPolicy restrictions:
Ensure the namespace’s NetworkPolicy allows ingress from the Zabbix server to the Service External IP. - Service External IP changes:
When recreating the LoadBalancer or restarting nodes, External IP may change.
Zabbix host settings must match the updated IP. - Pod readiness:
Even when a MySQL Pod is Running, if the readiness probe fails, the Pod disappears from the Service Endpoints, causing connection failure.
8. Conclusion
MySQL monitoring in Zabbix 7.4 can be summarized in one sentence:
As long as Agent2 has a correct DSN for MySQL, everything else works automatically.
- Plugin path:
/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.d/plugins.d/ - UserParameter is no longer needed (from Zabbix 6.0+)
- For Kubernetes: use External IP or NodePort
- Session-based config provides the best security and scalability
- Only one template is needed: “MySQL by Zabbix agent 2”
Whether MySQL runs on bare-metal or inside Pods does not matter.
When the DSN is correctly configured, Zabbix becomes a powerful, environment-agnostic MySQL monitoring platform.
🛠 마지막 수정일: 2025.12.12
ⓒ 2025 엉뚱한 녀석의 블로그 [quirky guy's Blog]. All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying or redistribution of the text and images is prohibited. When sharing, please include the original source link.
💡 도움이 필요하신가요?
Zabbix, Kubernetes, 그리고 다양한 오픈소스 인프라 환경에 대한 구축, 운영, 최적화, 장애 분석,
광고 및 협업 제안이 필요하다면 언제든 편하게 연락 주세요.
📧 Contact: jikimy75@gmail.com
💼 Service: 구축 대행 | 성능 튜닝 | 장애 분석 컨설팅
📖 E-BooK [PDF] 전자책 (Gumroad):
Zabbix 엔터프라이즈 최적화 핸드북
블로그에서 다룬 Zabbix 관련 글들을 기반으로 실무 중심의 지침서로 재구성했습니다.
운영 환경에서 바로 적용할 수 있는 최적화·트러블슈팅 노하우까지 모두 포함되어 있습니다.
💡 Need Professional Support?
If you need deployment, optimization, or troubleshooting support for Zabbix, Kubernetes,
or any other open-source infrastructure in your production environment, or if you are interested in
sponsorships, ads, or technical collaboration, feel free to contact me anytime.
📧 Email: jikimy75@gmail.com
💼 Services: Deployment Support | Performance Tuning | Incident Analysis Consulting
📖 PDF eBook (Gumroad):
Zabbix Enterprise Optimization Handbook
A single, production-ready PDF that compiles my in-depth Zabbix and Kubernetes monitoring guides.
답글 남기기
댓글을 달기 위해서는 로그인해야합니다.